Joint Ultrasound
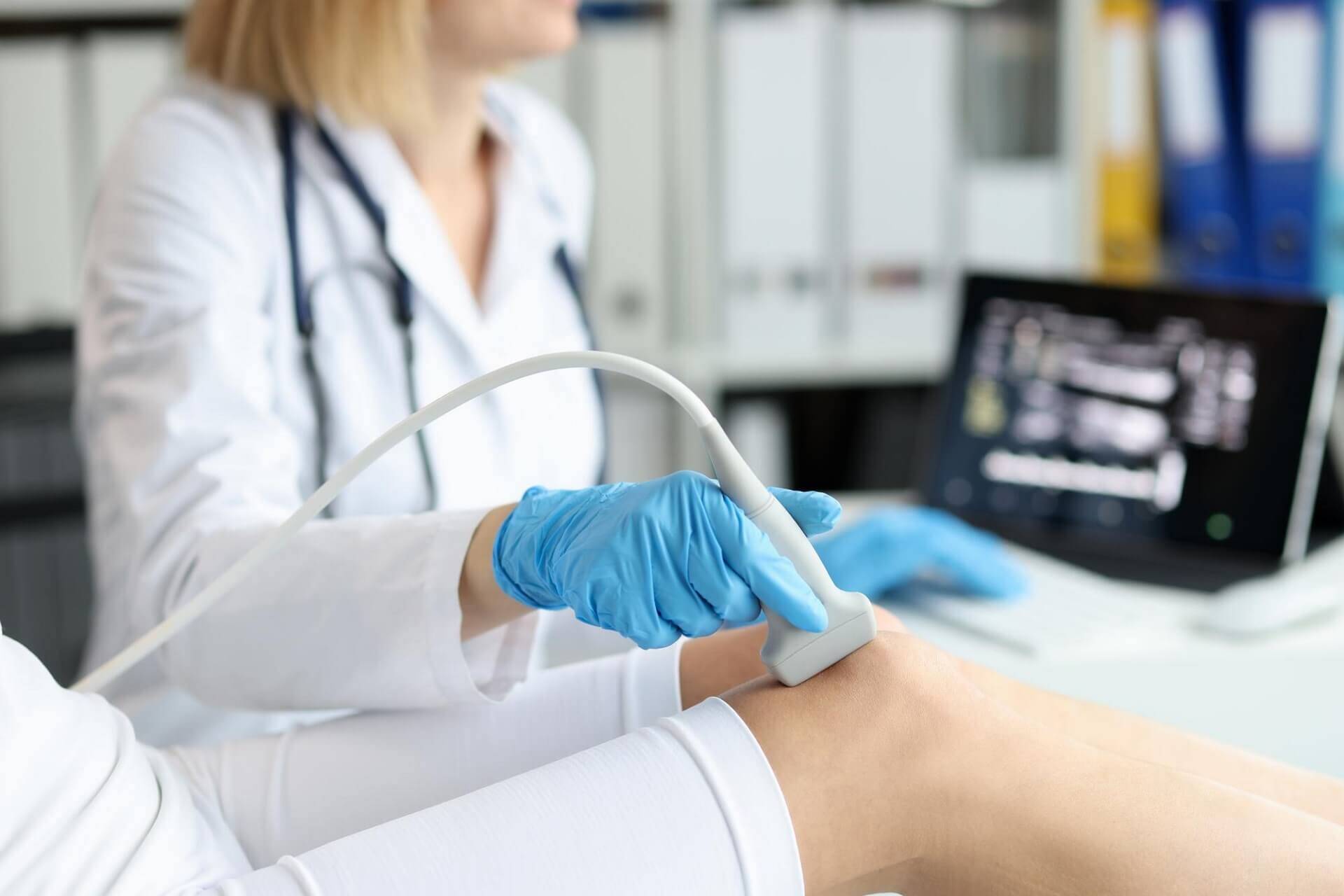
A joint ultrasound examination typically complements X-ray and CT scans. Various diagnostic methods are available to assess joint injuries and issues, one of which is ultrasound. During this procedure, the equipment emits ultrasound waves, and the reflected patterns create a two-dimensional image of the examined structures. It’s a painless, radiation-free method that requires no significant preparation.
Purpose of Joint Ultrasound Examination
X-rays and CT scans play a crucial role in diagnosing musculoskeletal injuries and problems. These two methods provide excellent images of hard bone tissues, revealing fractures, cracks, and the spatial relationships within the joint. However, sometimes the exact cause of the problem remains unclear. This is where joint ultrasound comes into play.
Joint ultrasound is highly effective in visualizing the cartilage, ligaments, and tendons within the joints. An additional advantage is that it can be used during movement, unlike X-rays and CT scans.
Joint ultrasound is also particularly useful for examining sports injuries.
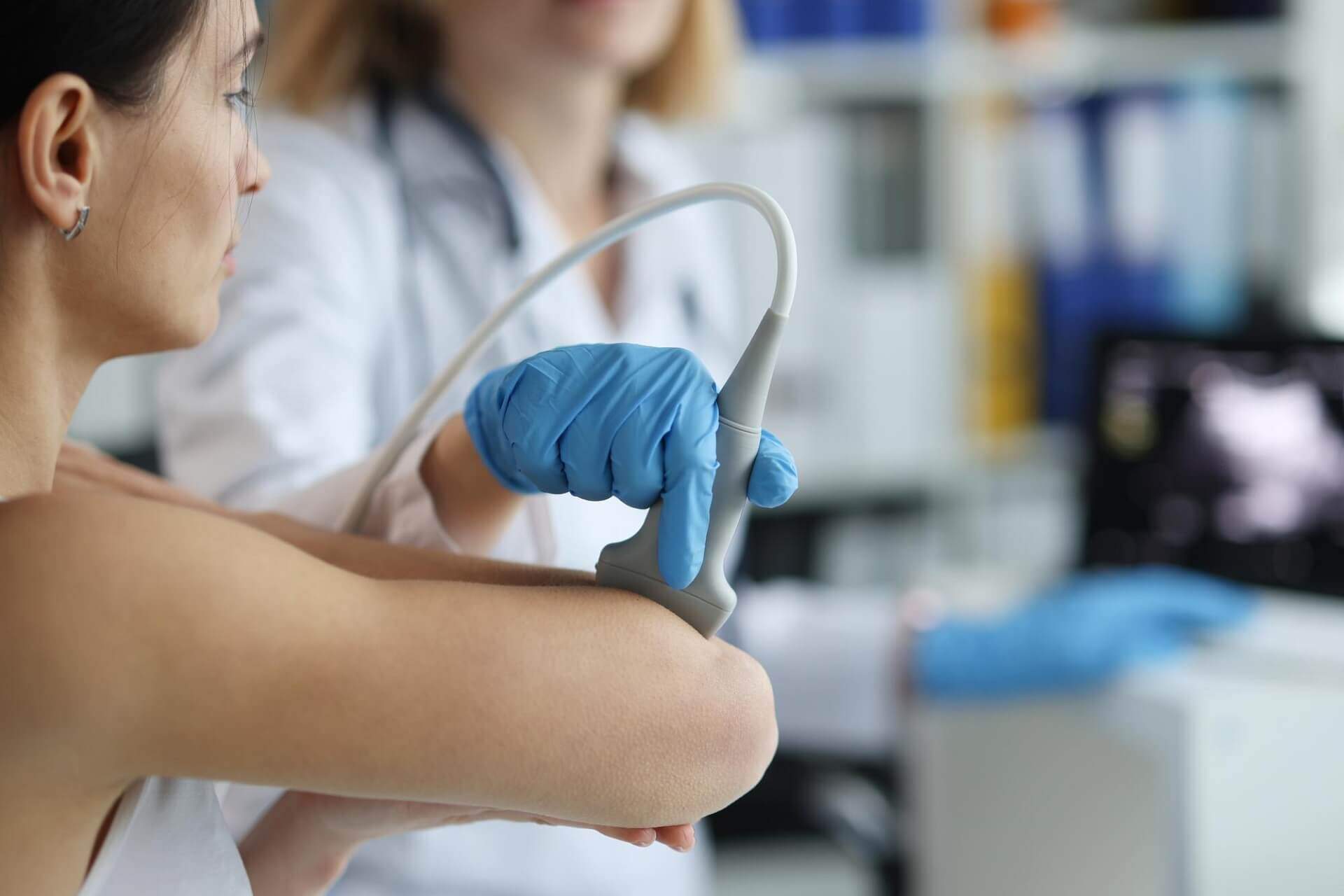
What Can Joint Ultrasound Diagnose?
Sports Injuries
Joint ultrasound is excellent for evaluating sports and other injuries. Various sprains, dislocations, and muscle or ligament tears may not be immediately apparent during a physical examination. Ultrasound can clearly show the condition of muscles and connective tissues, and bruising can be easily detected. It is effective for both acute and chronic sports injuries.
Post-Treatment Follow-Up
Joint ultrasound is often used for follow-up examinations after surgical interventions.
Hip Dysplasia
In infants, hip dysplasia can be detected via ultrasound as early as a few weeks old.
Degenerative Joint Diseases
In degenerative diseases, the articular cartilage covering the bones thins over time. Ultrasound can help determine the stage of the disease by showing the thickness and structure of the cartilage, as well as the joint space.
Inflammatory Diseases
Inflammatory diseases often result in fluid buildup, which can be easily detected with ultrasound. Thickening of the synovial membranes is also clearly visible.
Nerve Injuries
Many orthopedic conditions involve nerve damage. For example, in carpal tunnel syndrome, connective tissue painfully compresses the median nerve. Joint ultrasound is also a useful diagnostic tool in such cases.
Conditions and Process of Joint Ultrasound
Joint ultrasound does not involve radiation exposure and can be used on almost anyone. During the examination, the patient exposes the affected joint, and the doctor applies a special gel that enhances the device’s effectiveness. The doctor moves the probe to examine the tissues from different angles while the patient usually sits. The procedure is quick, typically lasting 20-30 minutes.
Joint Ultrasound at Újbuda Medical Center
If you already know you need an ultrasound, you can book an appointment using the link below! Our experienced orthopedic doctors will provide a detailed assessment of the problem and recommend appropriate treatment.
Preparations for the Ultrasound Examination
For abdominal and pelvic ultrasounds, refrain from eating for 6 hours before the examination, but drinking fluids is allowed and recommended—only non-carbonated and sugar-free fluids or water should be consumed. It is important to arrive with a full bladder for the exam.
For ultrasounds of other regions, no specific preparation is required.